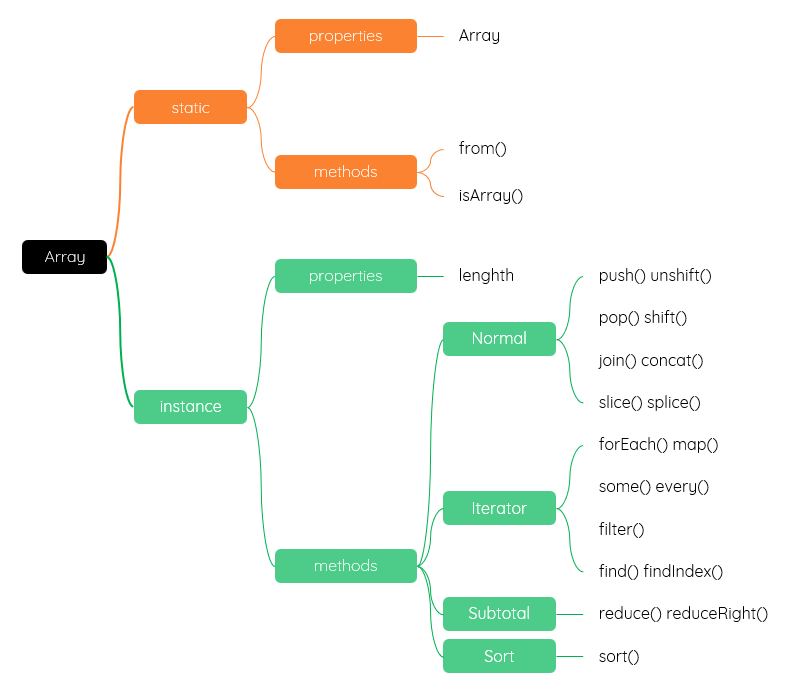

let arr0 = [1, 2, 3];
let arr1 = new Array(1, 2, 3);
console.log(arr0, arr1);
let arr0 = [1, 2]; let arr1 = arr0; arr1.push(3) arr0 = [1, 3];//指向别的内存
let [a, b] = [1, 3];
let [, , , , a] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; //a=5
[a, b] = [b, a];
let [name, age = 18, gender] = ['gl', , 'male'] let [name, age = 18] = ['gl']
let a = [1, 2, 3]; let b = [...a];
let [a, ...rest] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] //a=1 //rest=[2,3,4,5]
let a0 = [1, 2, 3] // 直接赋值;会彼此影响 let a1 = a0 a0.push(4) // 解构赋值:相当于重新赋值;不会彼此影响 let a2 = [...a0] a2.push(5) console.log(a0, a1, a2);
let obj0 = [{ id: 1, name: '张三' }, { id: 2, name: '李四' }, { id: 3, name: '王五' }]
console.log(obj0);
let obj1 = obj0
obj0.push({ id: 4, name: '赵六' })
let obj2 = [...obj0]
obj0.push({ id: 5, name: '老郭' })
obj2.push({ id: 5, name: '孙七' })
console.log(obj0, obj1, obj2);
console.log(typeof [1, 2]);//object console.log(Array.isArray([1, 2]));//true
| item | desc |
|---|---|
| push() | 添加元素到数组末尾 |
| unshift() | 添加元素到头部 |
| pop() | 移除数组末尾元素并返回 |
| shift() | 移除数组头部元素并返回 |
| concat() | 数组连接;返回一个新数组;不会修改原数组;不会去重 |
| join() | 数组元素按照指定的分隔符连接为字符串 |
| slice(start,end) |
Returns a copy of a section of an array.
取子串 - 选取串中位置|索引从 start 到 end 的部分;不包括 end
返回:一个新的数组/字符串
原数组:不变
start不指定,从0开始;end 不指定,截取到末尾
目标位置为负数时,反向截取;最后一位是-1;倒数第二位是-2,依次类推;可以用于获取后缀名;
|
| splice(start,count[,el...]) |
Removes elements from an array and, if necessary, inserts new elements in their place, returning the
deleted elements.
从原来数组中截取|删除指定长度的字符串
返回:删除的数据项
原数组:被修改
在删除的基础上,还可以插入新的元素el;如果 count 为0,则不删除
|
let arr0 = [1, 2, 3];
let arr1 = [3, 4, 5];
console.log(arr0.concat(arr1));//1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5
console.log(arr0);//1, 2, 3
console.log(arr0.join('-'));//1-2-3
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]; let res = arr.slice(2, 4); console.log(res);//3,4 console.log(arr);//不变
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]; let res = arr.splice(2, 2); console.log(res);//[3,4] console.log(arr);//[1,2,5,6,7,8,9] arr.splice(2, 1, 8, 8); console.log(arr);//[1,2,8,8,6,7,8,9];5被删除,插入|增加了2个8
function shuffle(arr) {
let tmp = [];
while (arr.length > 0) {
let rad = Math.floor(Math.random() * arr.length)
tmp.push(arr[rad])
arr.splice(rad, 1)
}
return tmp;
}
| item | desc |
|---|---|
| forEach() |
返回:没有
对数组中的每一项执行给定函数。本质上与使用 for 循环迭代数组一样
原数组:不会被修改;仅仅使用数据
无法中断
|
| map() |
对数组中的每一项执行给定函数,返回每次函数调用的结果组成的数组
适合创建包含的项与另一个数组一一对应的数组 - 映射
返回:新数组
原数组:不会被修改
|
| every() |
对数组中的每一项执行给定函数;如果该函数对 每一项 都返回 true,则返回 true
返回:布尔值
原数组:不会被修改
|
| some() |
对数组中的每一项执行给定函数;如果该函数 有一项 返回 true,则返回 true
返回类型:布尔值
原数组:不会被修改
|
| filter() |
对数组中的每一项执行给定函数,返回执行结果为 true 的项组成的数组 - calls the predicate function one time for each element in the
array
返回:符合条件的新数组
原数组:不会被修改
|
| find() |
查找满足提供的测试函数的 第一个 数据项
返回:查找到的数据项;若没有则返回 undefined
原数组:不会被修改
如果有,则立即返回;不会再继续测试后面的数据项
|
| findIndex() |
返回数组中满足提供的测试函数的 第一个 元素的索引
返回:查找到的数据项的索引;若没有找到对应元素则返回 -1
原数组:不会被修改
如果有,则立即返回;不会再继续测试后面的数据项
|
let data = [{ id: 10, name: 'gl' }, { id: 11, name: 'cq' }, { id: 12, name: 'sz' }]
let res = data.map(item => item.name)
let res = data.map(item => ({name: item.name, desc:item.desc}))
data.map(item => item.name = item.name.toUpperCase())
data.map(item => item.num = 1)
let data = ['gl', 'cq', 'sz', 'sh', 'gz']
let res = data.map((item, ind) => ({ id: ind, location: item }))
fetch('/utils/data/message.json')
.then(res => res.json())
.then(res => {
console.log(res);
let json = res.cont.map(item => `checkAll = options.every(item => item.check)
let arr = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5] let flag = arr.some(item => item > 5) console.log(flag); // false
let obj = [{ id: 10, name: 'gl' }, { id: 11, name: 'cq' }, { id: 12, name: 'sz' }]
let flag = obj.some(item => item.name == 'sz')
console.log(flag); // true
goods.filter(item => item.name.includes(keyword))
let arr = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] let res = arr.filter(item => item % 2 === 0)
let data = [{ id: 10, name: 'gl' }, { id: 11, name: 'cq' }, { id: 12, name: 'sz' }]
let res = data.filter(item => item.id != 11)
function delItem(dataItem) {
data = data.filter(item => item.id != dataItem.id)
}
let obj = [{ id: 10, name: 'gl' }, { id: 11, name: 'cq' }, { id: 12, name: 'sz' }]
let res = obj.find(item => item.id === 11)
console.log(res); // { id: 11, name: 'cq' }
const existingItem = cart.find(item => item.id === product.id)
if (existingItem) {
existingItem.quantity++
} else {
cart.push({ ...product, quantity: 1 })
}
| item | desc |
|---|---|
| reduce() | reduce()方法从数组的第一项开始,逐个遍历到最后 |
| reduceRight() | 从数组的最后一项开始,向前遍历到第一项 |
let sum = arr.reduce((pre, cur, index, array) => {
return pre + cur;
})
let sum = goods.reduce((total, item) => {
return total + item.price + item.quantity;
}, 0)
| item | desc |
|---|---|
| sort() |
不指定比较函数
默认根据数据项 UTF-16 编码升序比较 - The default sort order is ascending
|
| sort(compareFn) | 指定比较函数 - 按照参数进行排序 |
const arr = [1,45,6,2,4,5] //升序 arr.sort(); //[1, 2, 4, 45, 5, 6] //降序 arr.sort().reverse(); //[6, 5, 45, 4, 2, 1]
const arr = ['banana', 'apple', 'cherry']; arr.sort(); // ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
arr = [1,45,6,2,4,5] //升序 arr.sort((a, b) => a - b); //[1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 45] //降序 arr.sort((a, b) => b - a); //[45, 6, 5, 4, 2, 1]
//升序 obj.sort((a, b) => a['age'] - b['age']); //降序 obj.sort((a, b) => b['age'] - a['age']);
const sortUp = (key) => {
arr.sort((a, b) => {
return a[key] - b[key]
})
}
const sortDown = (key) => {
arr.sort((a, b) => {
return b[key] - a[key]
})
}
obj.sort((a, b) => {
return a.name.localeCompare(b.name)
})
obj.sort((a, b) => {
return b.name.localeCompare(a.name)
})